Introduction to System Software
Lecture 1
System Software is computer software designed to
Operate and control the computer hardware
Provide a platform for running application software
System software includes the following:
Operating system, allows the parts of a computer to work together and also provides a platform to run high-level system software and application software
Utility software, helps to analyze, configure, optimize and maintain the computer
Device drivers, like BIOS and device firmware provide basic functionality to operate and control the hardware
A user interface
Sometimes developer tools
What is an Operating System?
An intermediary between a user of a computer and the computer hardware
Goals to execute user programs and make solving user problems easier
Goals to make the computer system convenient to use
Goals to use the computer hardware in an efficient manner
Operating System Definition
OS is a resource allocator
Manages all resources
Decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resources use
OS is a control program
Controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of the computer
Kernel-The program running at all times on the computer
Computer Startup
Bootstrap program is loaded at power-up or reboot
Typically stored in ROM or EPROM, generally known as firmware
Initializes all aspects of system
Loads operating system kernel and starts excution
Lecture2
Computer System & OS Structures
Computer System Operation
I/O Structure
Storage Structure, Storage Hierarchy
Hardware Protection
Operating System Services, System calls, System Programs
Structuring OS
Virtual Machine Struction and Organization
OS Design and Implementation
Process Management, Memory Management, Secondary Storage Management, I/O System Management, File Management, Protection System, Networking, Command-Interpreter.
Computer System Organization
Computer-system operation
One or more CPUs, device controllers connect through common bus providing access to shared memory
Concurrent execution of CPUs and devices competing for memory cycles
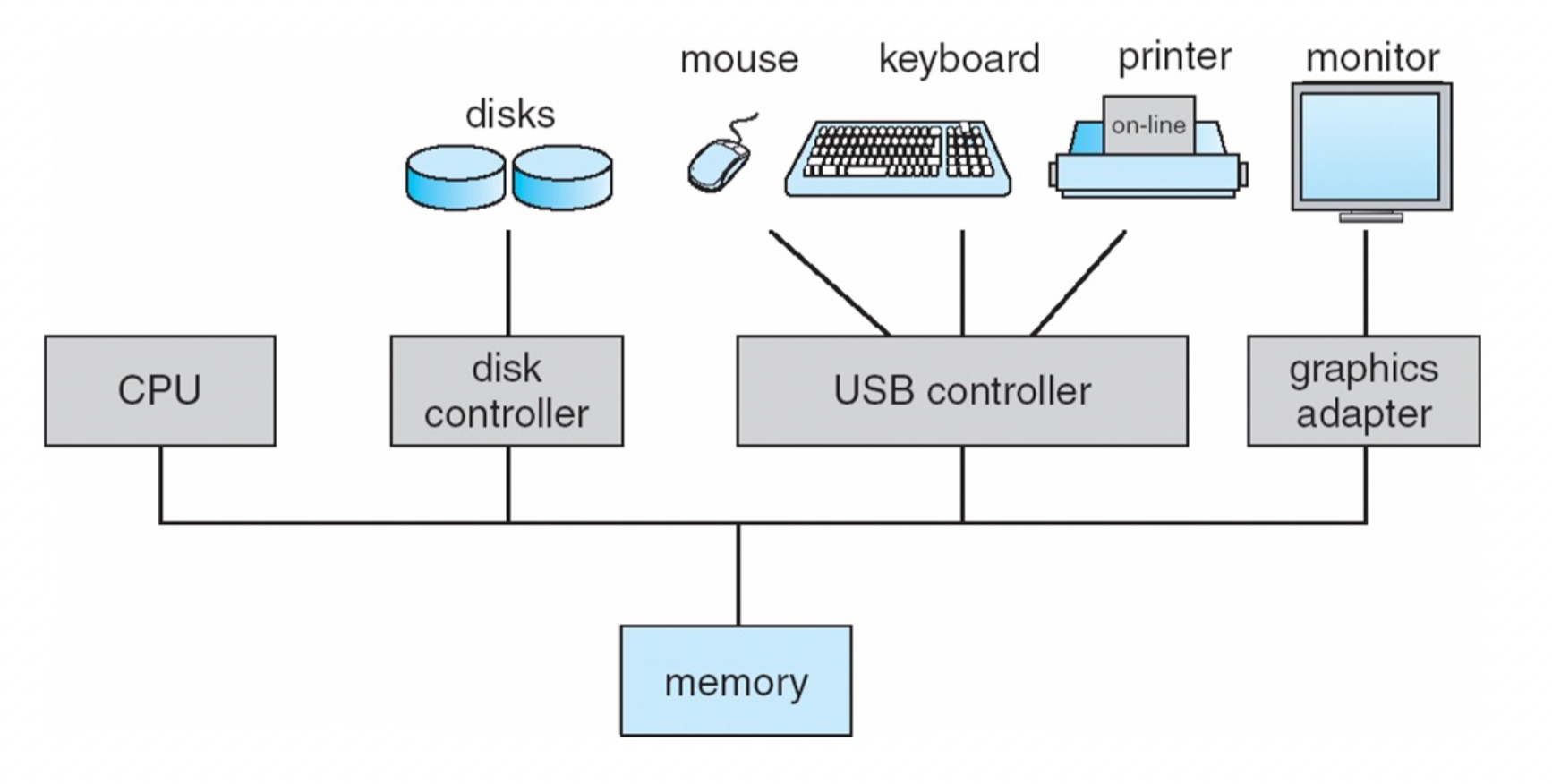
Computer-System Operation
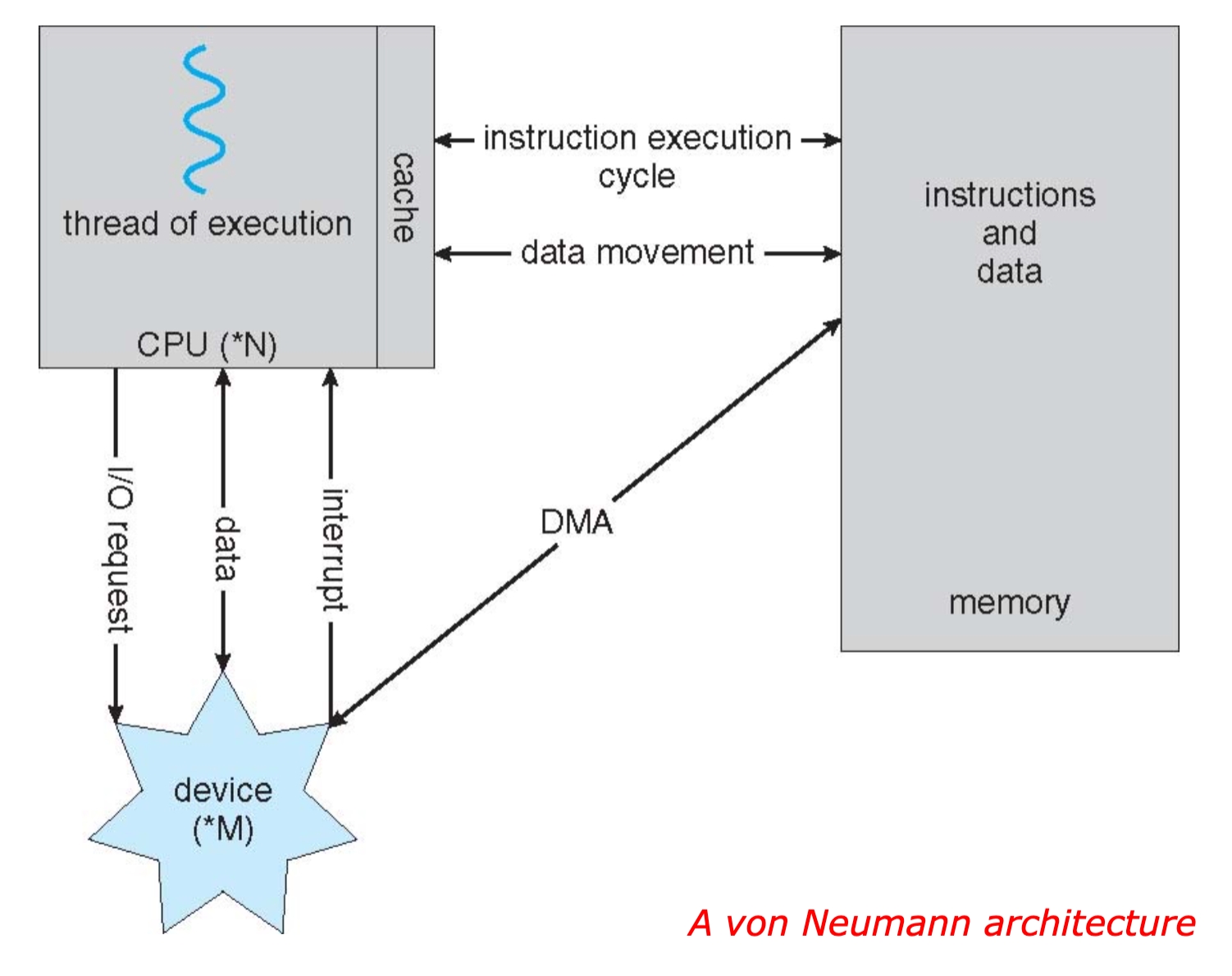
I/O devices and athe CPU can execute concurrently
Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type
Each device controller has a local buffer
CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers
I/O is from the devices to local buffer of controller
Devices controller informs CPU that it has finished its operation by raising an interrupt
Common Functions of Interrupts
Interrupt transfers control to the interrupt service routine, generally through the interrupt vector, which contains the addresses of all the services routines (jump)
Interrupt architecture must save the address of the interruptted instruction
Incoming interrupts are disabled while another interrupt is being processed to prevent a lost interrupt
An operating system is interrupt driven
A polled interrupt requires that the interrupt handler poll or send a signal to each device in turn in handler poll or send a signal to each device in turn in order to find to which one sent the interrupt request
I/O Structure
Synchronous I/O (blocking I/O):
After I/O starts, control return to user program only upon I/O completion
wait instruction idles CPU until next interrupt
no simultaneous I/O processing, at most one outstanding I/O request at a time
Asynchronous I/O (non-blocking I/O):
after I.O starts, control returs to user program without waiting for I/O completion
System call
Device Status table - holds type, address and state for each device
OS indexes into I/O device table to determine device status and modify table entry include interrupt
Direct Memory Access Structure
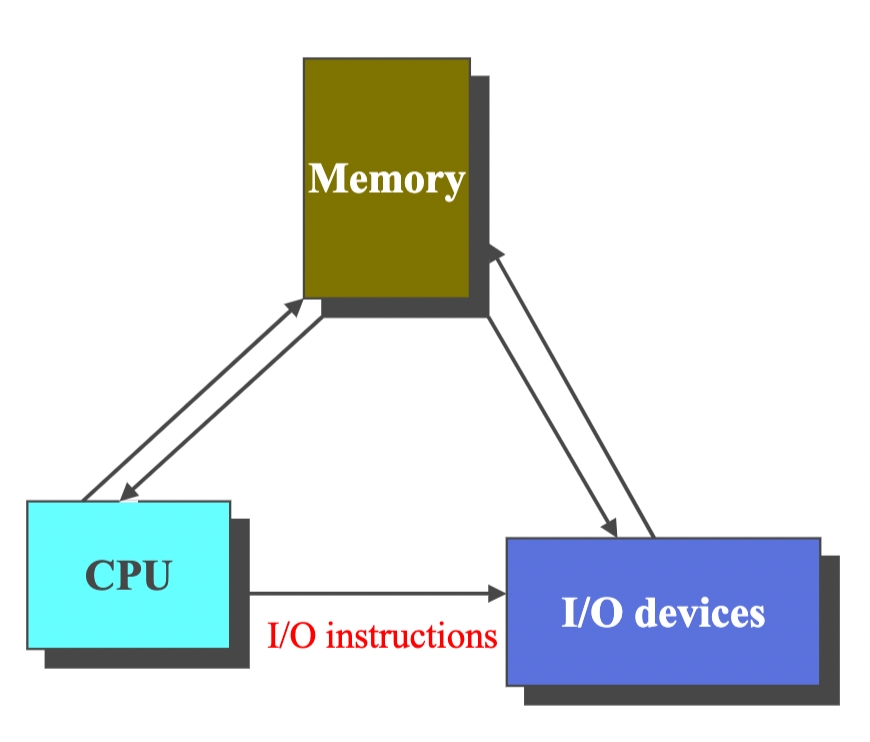
DMA: Direct Memory Access
How a Modern Computer Works?
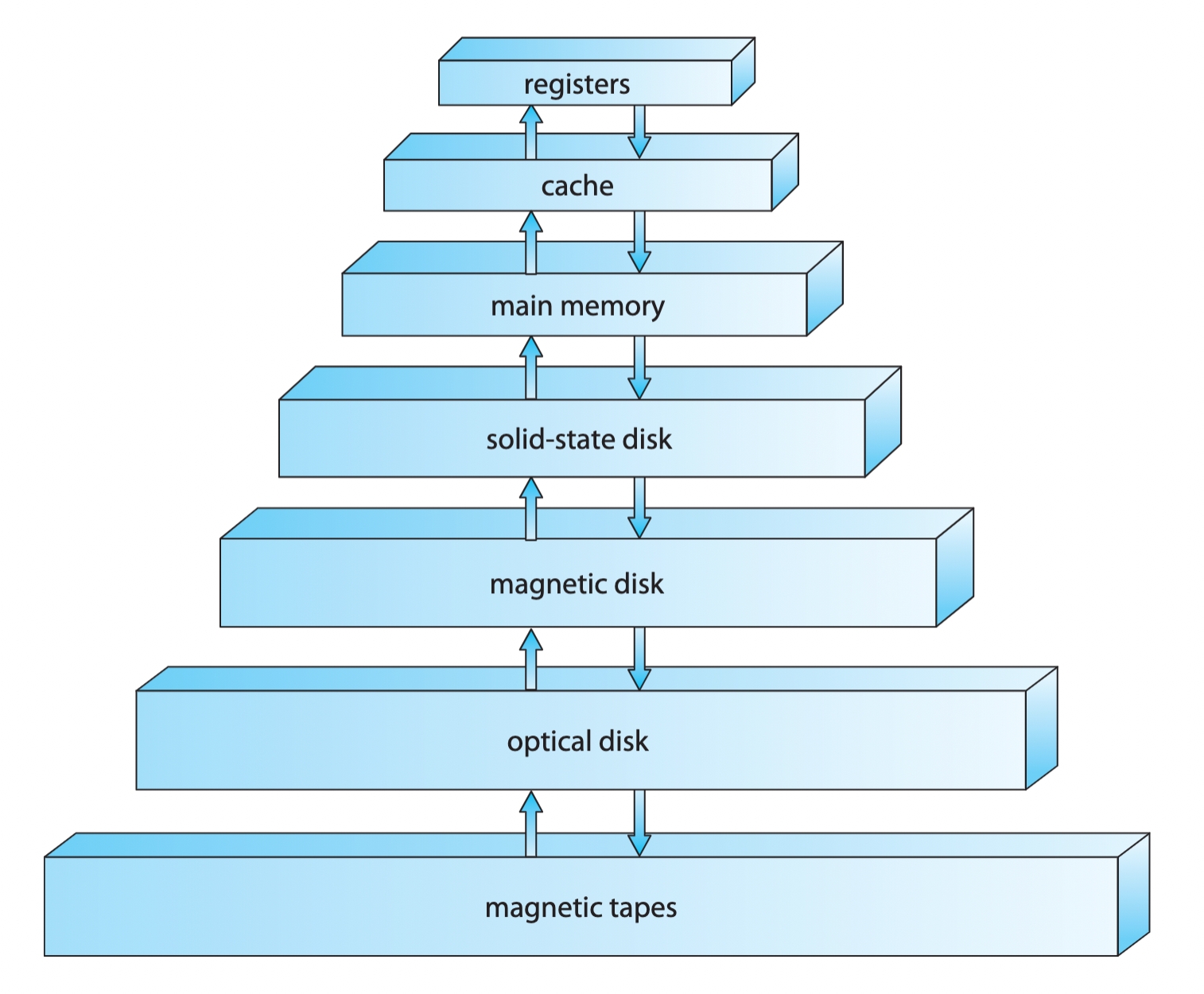
Storage Hierarchy
Storage systems organized in herarchy based on
Speed
Cost
Volatility
Caching is often used between storage systems
transparently copying information into faster storage system (e.g. CPU cache holds most-recently used data from main memory)
main memory can be viewed as a cache for secondary storage
CPU Protection
Timer - interrupts computer after specified period to ensure that OS maintain control
Timer is decremented every clock tick
When timer reaches a value of 0, an interrupt occurs
Timer is commonly used to implement time sharing
Timer is also used to compute the current time
Load timer is a privileged instruction
Last updated
Was this helpful?